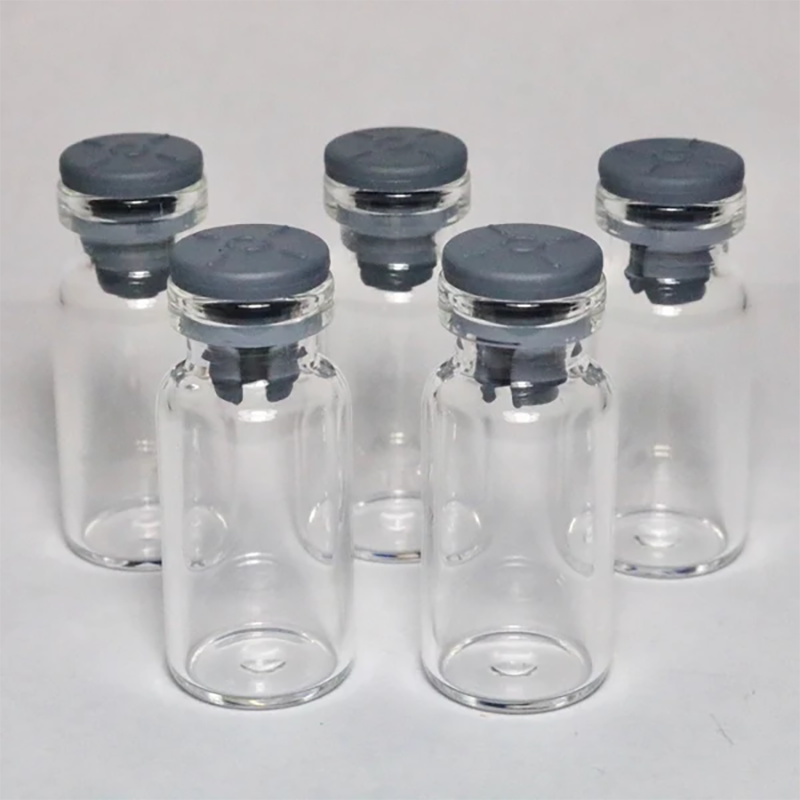
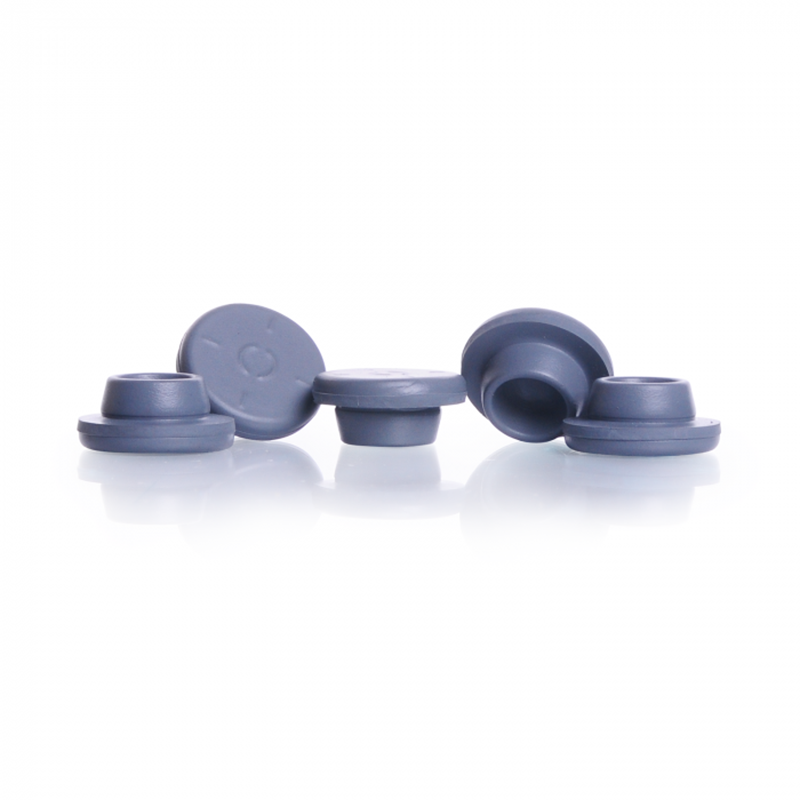
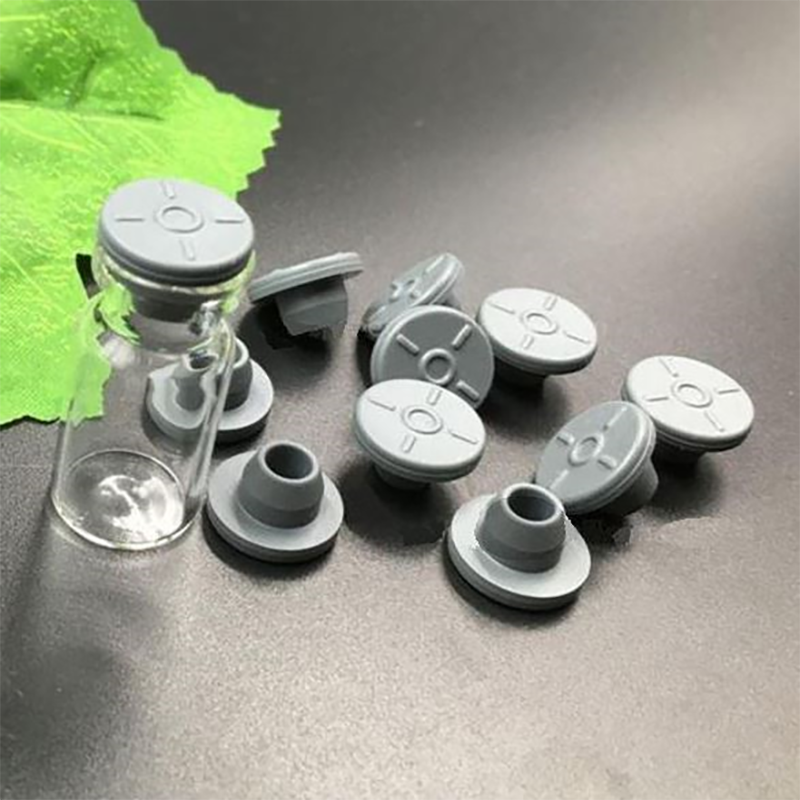
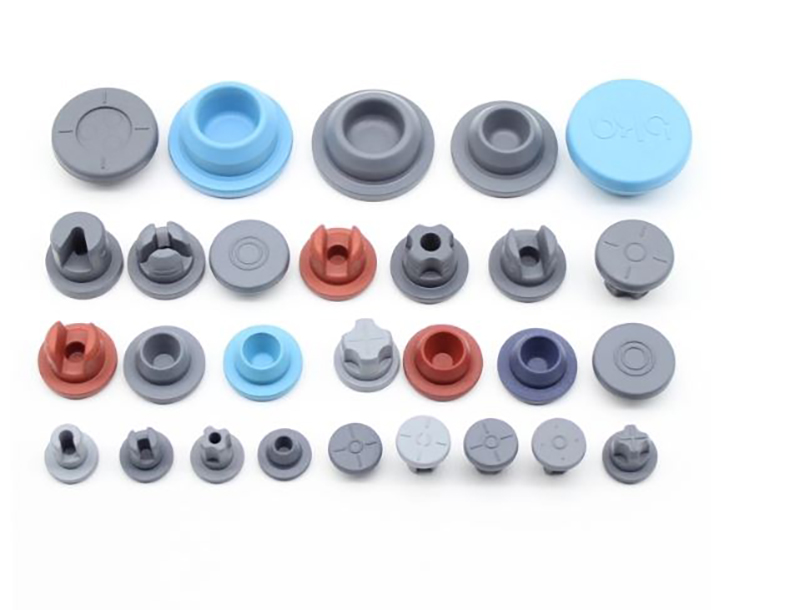
Vials Butyl Rubber Stopper
Butyl Rubber Septa Stoppers are widely used in laboratory and medical applications due to their outstanding sealing performance, corrosion resistance, and hygiene, ensuring the quality and safety of pharmaceuticals, reagents, and samples.
- Excellent sealing performance: Butyl rubber septa stoppers provide outstanding sealing performance, effectively preventing the entry of moisture, oxygen, and other contaminants from the external environment, thus maintaining the purity and effectiveness of pharmaceuticals, reagents, or samples.
- Chemical resistance: Butyl rubber exhibits excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, making it capable of withstanding various pharmaceuticals, reagents, and solvents without being easily corroded by chemical substances, ensuring the reliability of the stopper in various laboratory environments.
- Good elasticity: Butyl rubber possesses excellent elasticity, allowing it to adapt to various shapes and sizes of container openings, ensuring a tight fit and a reliable seal without the need for additional securing devices.
- Longevity: Butyl rubber septa stoppers typically have a long lifespan as they are resistant to aging and damage, allowing for multiple uses and reducing the need for frequent replacements and associated costs.
- Non-toxic and hygienic: Butyl rubber is a safe material that does not release harmful substances, making it suitable for pharmaceutical and laboratory applications, particularly in environments where stringent hygiene control is necessary.
- Wide temperature range: Butyl rubber septa stoppers can operate effectively across a wide temperature range, from extremely low temperatures to relatively high temperatures, making them suitable for various experimental conditions.
- Versatility: They can be used to seal a variety of containers such as vials, bottle necks, reagent bottles, and sample bottles, ensuring the integrity of samples and reagents.

Manufacturing Process
- Raw Material Preparation:
- Select high-quality rubber or silicone materials that meet hygiene and quality standards.
- Raw materials are typically supplied in pellet or sheet form and may require initial processing and blending to obtain the desired properties.
- Compound Preparation:
- Add appropriate additives and curing agents to the rubber material to ensure it can achieve the required properties during the subsequent curing process.
- Mix the rubber material to ensure even distribution of additives and curing agents.
- Molding:
- Utilize injection molding or extrusion molding processes to shape the rubber material into the desired form of stoppers.
- Post-molding products may require a curing or cross-linking process to enhance their strength and corrosion resistance.
- Inspection and Testing:
- Perform quality inspection and testing on each manufactured Rubber Medicine Bottle Stopper. This includes visual inspection, dimensional measurements, hardness testing, and sealing performance tests.
- Various methods such as pressure testing, leak testing, and tensile testing can be used to validate the stopper’s performance.
- Surface Treatment:
- Apply surface treatments, such as silicone oil lubrication or UV irradiation, as needed to improve performance and usability.
- Packaging:
- Use suitable packaging materials to ensure that Rubber Medicine Bottle Stoppers remain undamaged and uncontaminated during transportation and storage.
- To aid user identification and usage, relevant information like production dates, model numbers, batch numbers, etc., can be labeled on the packaging.
- Quality Control:
- Implement quality control measures to monitor each step of the production process to ensure that products meet relevant quality standards and regulations.
- Cleaning and Sterilization:
- In pharmaceutical or medical applications, Rubber Medicine Bottle Stoppers may require proper cleaning and sterilization to ensure hygiene.
The above steps represent a general outline of the manufacturing process for Rubber Medicine Bottle Stoppers. The actual production process may vary depending on manufacturing equipment, product specifications, and application requirements. Quality control is critical throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product performance and safety. Additionally, adherence to relevant hygiene standards and regulations, especially in the pharmaceutical and medical fields, is essential.



- Size and Shape
- Performance Requirements
- Material Selection
- Custom Printing and Labeling
- Packaging Requirements
- Rapid Response
- Technical Support
With these customization capabilities, manufacturers can collaborate with clients from various industries, meeting their specific requirements by delivering highly tailored products. This establishes long-term partnerships and sets them apart in the competitive market. Such capabilities are crucial for meeting evolving market demands