In the world of industrial design and manufacturing, selecting the right material is crucial to ensuring the longevity and performance of a product. When it comes to applications that involve high temperatures, not all plastics are created equal. Some plastics can withstand moderate heat, while others are specifically engineered to endure extreme conditions without compromising their integrity. At YJCPolymer, we understand that finding the right heat-resistant plastic for your project can be challenging, but we’re here to help. In this blog, we’ll dive into the various heat-resistant polymers available today and provide you with the insights you need to make an informed decision.
Understanding Heat-Resistant Plastics: What Does “Heat-Resistant” Mean?
When we refer to a plastic as “heat-resistant,” we are talking about its ability to maintain its structural integrity under high temperatures. For most engineering plastics, this means withstanding temperatures in the range of 180°F to 350°F (82°C to 177°C). However, for high-performance applications, you may need materials that can endure temperatures well beyond that range. It’s essential to define your application’s temperature requirements in order to select a plastic that can handle the specific heat exposure without degrading or losing its strength.
At YJCPolymer, we specialize in high-performance polymers that can handle high temperatures, and we have the experience and expertise to guide you through the selection process to ensure you choose the right material for your specific needs.
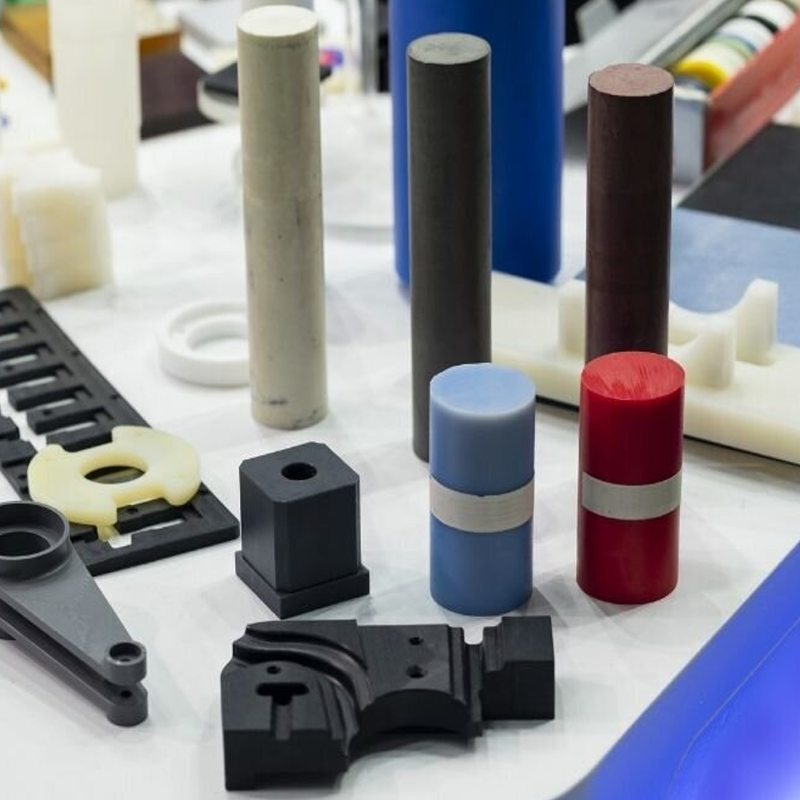

Types of Heat-Resistant Plastics
There are several types of plastics that are engineered to withstand high temperatures, each offering unique characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. Here’s an overview of some of the most common heat-resistant plastics:
1. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) – Teflon
Perhaps the most well-known heat-resistant plastic, PTFE, commonly referred to as Teflon, is known for its exceptional thermal stability and resistance to chemicals. With a continuous service temperature of up to 500°F (260°C), PTFE is used in a variety of industries, from non-stick cookware to mechanical components like bearing blocks and housings. It’s hydrophobic, extremely slippery, and boasts one of the lowest coefficients of friction, making it perfect for applications that require high durability and minimal wear.
One of the unique properties of PTFE is its resistance to acids and solvents, which makes it ideal for harsh environments. However, PTFE cannot be injection-molded or 3D-printed, making machining a preferable method of fabrication.

2. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
For applications that require both thermal stability and machinability, PEEK is one of the most sought-after materials. This high-performance thermoplastic has a melting point near that of PTFE, with a continuous working temperature of up to 482°F (250°C). PEEK retains its mechanical properties at high temperatures and is resistant to radiation, chemicals, and hydrolysis, making it ideal for a variety of demanding applications, including those in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
Not only is PEEK injection moldable and machinable, but it is also autoclave-sterilizable, making it an excellent choice for medical devices such as spinal implants. Its high strength-to-weight ratio and durability make it an attractive alternative to metal alloys in some high-performance applications, such as in aircraft components.
3. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS)
PPS, often sold under the brand name Ryton, is another high-temperature polymer, with a working temperature of 428°F (220°C). It offers a combination of good mechanical strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and dielectric properties, making it ideal for use in automotive and electrical applications. It is also resistant to most solvents and chemicals, ensuring that it can endure harsh environments.
While PPS is not typically used for machined parts, PPSU (Polyphenylsulfone) is a similar material that can be machined and has a comparable temperature range. PPSU is often used in the aerospace and medical industries, offering excellent durability and resistance to high temperatures and sterilization.
4. Polyetherimide (PEI) – Ultem
With a maximum continuous operating temperature of 340°F (171°C), Ultem is an excellent polymer for applications that require high strength, rigidity, and excellent dielectric properties. PEI is available in various glass-filled levels, which enhances its mechanical properties. While it is not suitable for extremely high-temperature applications, it remains a great all-around material for use in automotive, electrical, and aerospace applications.
Ultem is also machinable and can be used in injection molding processes, making it a versatile choice for manufacturing parts that must perform well under moderate heat conditions.
High-Temperature 3D Printing Materials
As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, the range of high-temperature plastics available for additive manufacturing has also expanded. For instance, the advanced high-temp stereolithography resin known as PerFORM can withstand temperatures of up to 514°F (268°C) after post-curing. This material is ideal for applications such as wind tunnel testing, rapid prototyping, and electronic housings.
Another notable high-temperature 3D printing material is Accura 5530, a PC-like resin that combines optical clarity with good heat resistance. It’s ideal for applications that require transparency and durability, as well as resistance to water, chemicals, fire, and electrical effects.
Selecting the Right Heat-Resistant Plastic
Choosing the appropriate heat-resistant plastic for your application requires considering a few key factors, including:
- Operating Temperature: How much heat will the plastic be exposed to during its lifecycle? Be sure to choose a plastic with a working temperature that meets or exceeds your requirements.
- Chemical Resistance: Will the plastic be exposed to harsh chemicals, oils, or solvents? Some high-temperature plastics offer better chemical resistance than others.
- Mechanical Properties: Does the plastic need to withstand significant mechanical stress or pressure? Materials like PEEK and PPS offer excellent mechanical strength at high temperatures.
- Manufacturing Process: Will the plastic be molded, machined, or 3D printed? Some materials, such as PTFE, are best suited for machining, while others like PEEK are both machinable and injection-moldable.
At YJCPolymer, we offer a wide range of high-temperature plastics, including many of the materials discussed above, and our team of experts is ready to help you choose the best option for your specific needs.

Final Thoughts
Heat-resistant plastics are essential for applications that involve high temperatures, but choosing the right material can be complex. Understanding the properties of different polymers, such as PTFE, PEEK, PPS, and Ultem, is crucial to ensuring you select the right plastic for your application. Whether you’re designing parts for the aerospace, automotive, or medical industries, YJCPolymer has the expertise and resources to help you make the best choice.
If you’re looking for high-performance heat-resistant plastics for your next project, don’t hesitate to reach out to YJCPolymer. Our team is ready to provide you with the materials, insights, and support you need to bring your vision to life. Contact us today for a quote, and let’s get started on finding the perfect solution for your high-temperature applications!