Guys, guess what interesting topic we brought to you today lol, because I think you have a basic understanding of LSR, but the advantages of LSR are still not well understood, so let’s spend a little time discussing them today.
Manufacturers across industries use plastics in injection molding for their strength, lightweight properties, and malleability. However, materials like thermoplastic elastomers face limitations in high temperatures, prompting a shift to liquid silicone rubber. Its superior heat resistance ensures structural integrity under elevated conditions.
What is liquid silicone rubber?
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) constitutes a two-part silicone-based polymer intricately bonded through a chemical amalgamation. Predominantly employed in the manufacturing of injection-molded components, LSR finds application in diverse industries such as automotive, food, appliances, textiles, and consumer goods.
Upon subjecting the polymer to the injection molding process and subsequent heating, the catalyst instigates a cross-linking reaction. This reaction imparts enduring strength and shape to the material during the curing phase.
The resultant LSR material boasts robustness and longevity, rendering it well-suited for an array of applications, notably:
- Precision appliance hardware components
- Automotive parts characterized by intricate design specifications
- Electronic interfaces demanding high-performance properties
- O-rings, where resilience and durability are paramount
What are the advantages of using liquid silicone rubber?
- Exceptional Thermal Stability:
Liquid Silicone Rubbers (LSRs) exhibit remarkable resistance to temperatures up to 180 °C without succumbing to melting or creeping, making them a preferred choice for demanding applications in heavy-duty and automotive sectors, such as seals and gaskets.
- Cold Flexibility:
Unlike thermoplastic elastomers, which can lose flexibility in extremely low temperatures, LSRs remain pliable even at -50 °C, making them ideal for products requiring operation in frigid environments.
- Aging Resistance:
Cured LSR materials showcase excellent resistance to UV rays, weathering, and aging, ensuring longevity and reliability, particularly in applications subjected to prolonged exposure to the elements.
- Chemical Resistance:
While thermoplastic elastomers offer chemical resistance within moderate temperature ranges, LSRs excel with low water absorption and robust resistance to common chemicals, even under extreme temperature conditions.
- Low Compression Set:
LSRs exhibit a remarkably low compression set (typically 15%-20%), signifying their ability to resist permanent deformation under constant strain. This characteristic allows them to maintain elasticity even when compressed over extended durations and across varying temperature ranges.
- Reliable Shelf Life:
Liquid Silicone Rubber boasts a significant shelf life, typically lasting at least one year, contributing to its ease of use in manufacturing environments.
The above is the relevant introduction of LSR. Finally, I would like to add some pictures of our factory to see the operation process of LSR more intuitively, and show you a general tour of our machines.
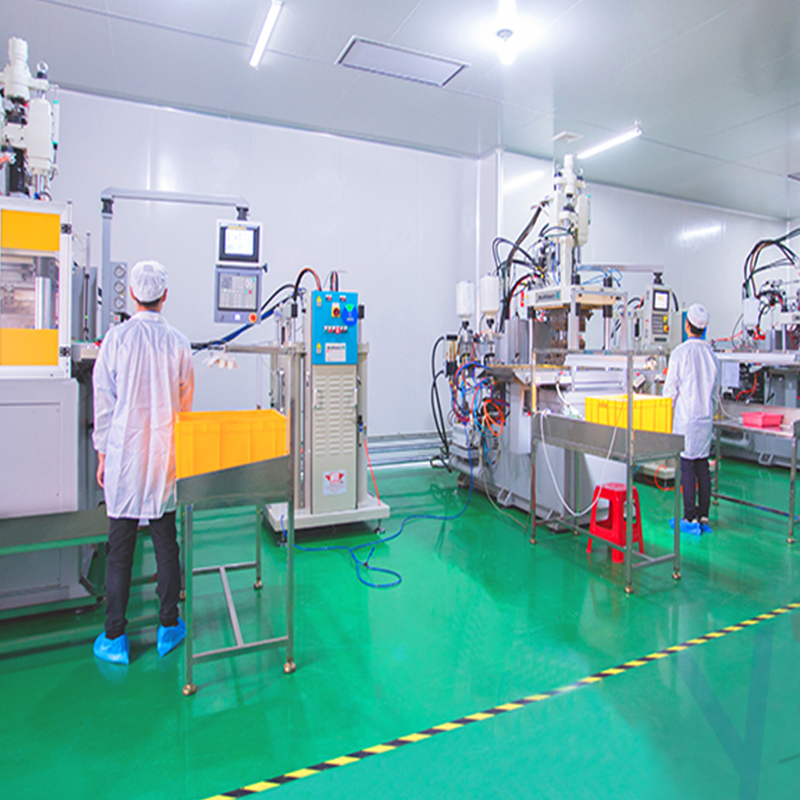

Well, guys, that’s all for today, if you have any other thoughts, feel free to leave a comment below!